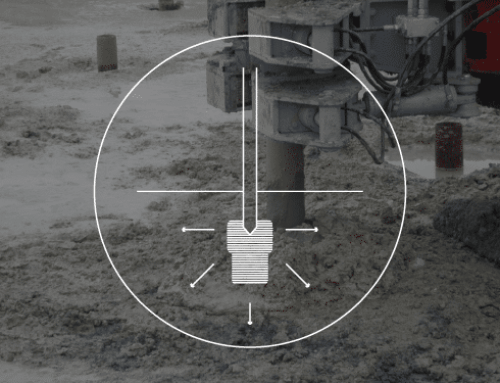
Earthquake (EQ) drains are used to mitigate/limit the effects of seismically-induced liquefaction by allowing for the rapid dissipation of excess porewater pressures generated by seismic events.
During earthquakes, a phenomenon known as liquefaction can occur when pore water pressures increase because of seismic motions. Granular soils such as sands are most prone to liquefaction, and the effects can include loss of shear strength, lateral spreading, excessive settlement, and even bearing capacity failures.
Key Elements
WHAT ARE THEY?
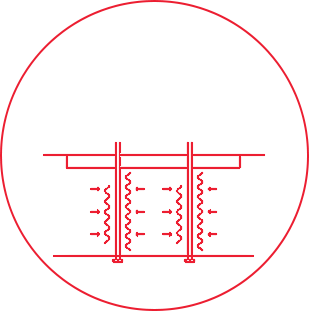
Slotted, flexible, corrugated plastic pipe wrapped in a filter fabric installed with a vibrating mandrel in a grid pattern.
HOW DO THEY WORK?
Their flow capacity allows a path for excess pore pressure to rapidly dissipate during an earthquake, providing sufficient discharge capacity to mitigate liquefaction and reduce post-earthquake settlement.
WHY USE THEM?
To quickly reduce excess pore water pressure generated by earthquake loading, hence mitigating the risk of liquefaction.
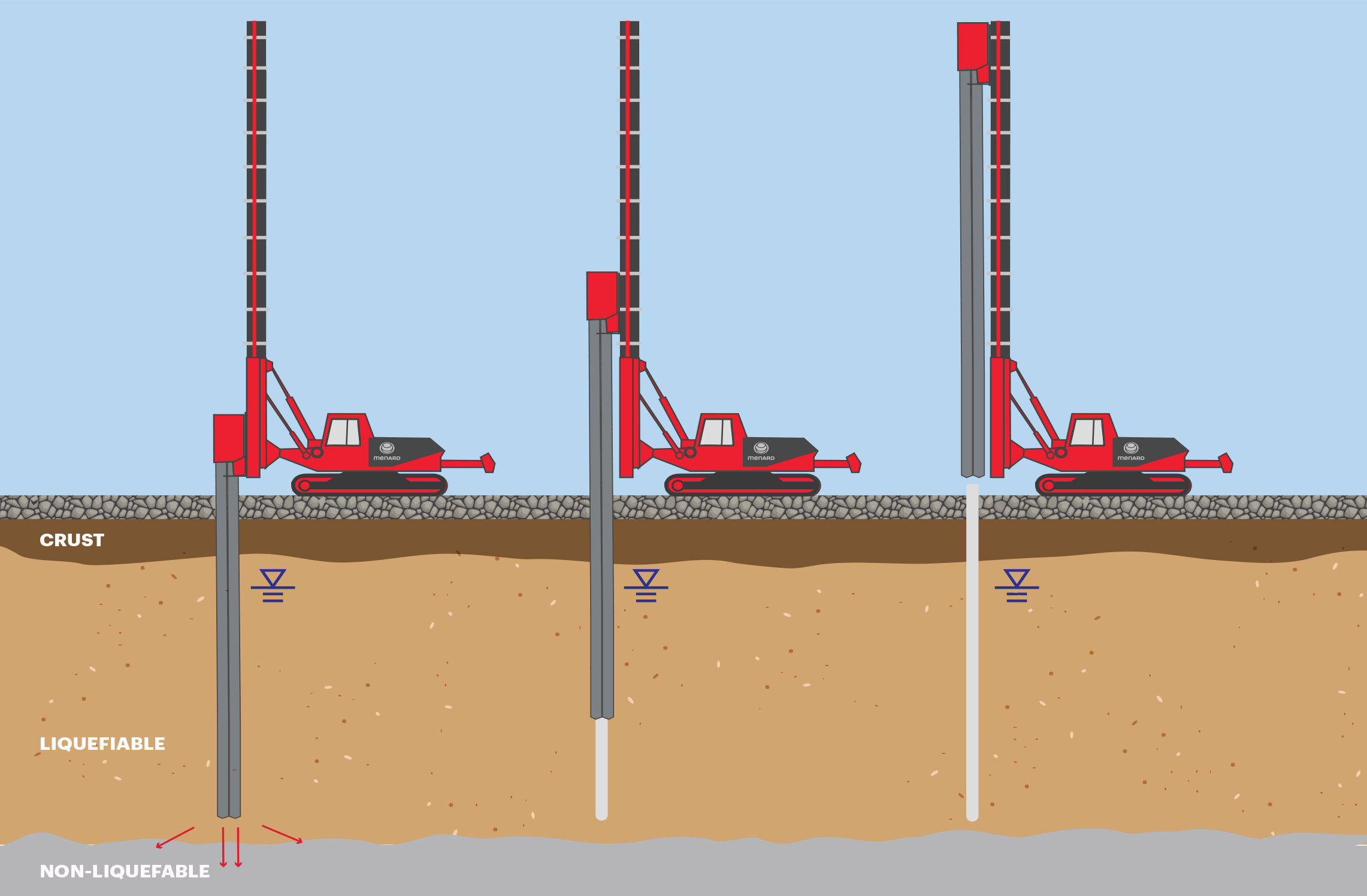
Earthquake (EQ) drains are slotted, corrugated pipes that are encased in a geotextile fabric wrap. The drains are typically vibrated into the ground and are designed to dissipate pore pressure during seismic events.
Advantages of EQ Drains Include:
- Simple installation process
- Economical and environmentally-sustainable solution as compared to other ground improvement approaches that require relatively expensive materials such as stone and cement
- Readily installed to depths of 55 ft
- Minimal spoils are generated when installed using driven displacement methods
- Densification of surrounding soils in some cases when installed using vibratory/displacement methods
- Installation techniques can be modified to protect vibration-sensitive sites/structures
Download our earthquake drains technique sheet: